Phosphating is a chemical pre-treatment that is applied to metals in order to protect them from corrosive agents. Let’s see why it is essential for coating and why we always recommend its use.
If you are wondering what phosphating is and why it is considered by many to be an essential step on the path towards full protection of a metal article from external agents, we will answer your questions today.
First of all, phosphating is a fundamental process for the success of an industrial coating treatment, and not only that. It is part of a wider process that leads to extending the useful life of an asset and ultimately increasing its value over time.
First, we need to understand what it consists of and how it is implemented.
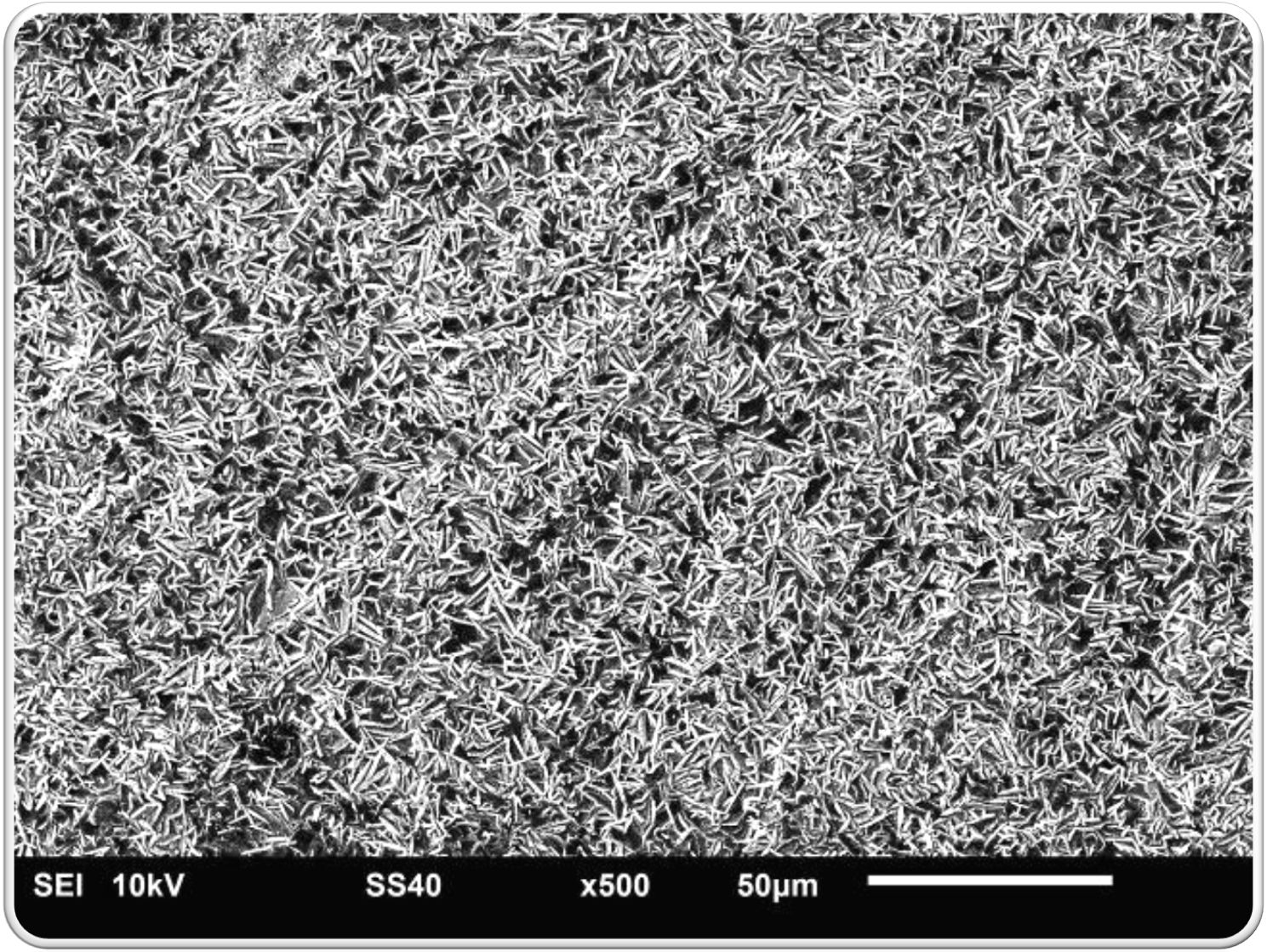
What is Phosphate Conversion Coating
Phosphating is a chemical process characterised by the reaction between sulphuric acid and the metal surface, with subsequent deposition of the zinc layer as a protective barrier against corrosion.
It can be applied to steel, iron, cast iron, aluminium and metal alloys and leads to the formation of a layer consisting of insoluble phosphates that create a protective layer against external agents. It is a chemical conversion, i.e. a process that leads to a change in the chemical composition of the surface of a metal.
In order to achieve the best possible results, our coating lines include zinc phosphating, applied by spray.
The article to be treated is invested with a chemical solution applied by spray, composed of various elements, including:
- Zinc phosphate;
- Free phosphoric acid;
- Accelerants, which are intended to speed up the chemical reaction;
- Other additives, such as manganese, calcium, fluorides, etc. Each of these additives makes a specific contribution, for example to make the surface crystalline grain finer and more compact in order to improve corrosion resistance.
Treatments before phosphating
Since the quality of the phosphating process is directly related to the condition of the surface to be coated, it must be prepared in the best possible way.
This means that before starting the phosphating process, the metal items must be perfectly clean: oil and grease, traces of oxidation, scale and various impurities must be removed.
This is why the process is preceded by a series of stages, including:
- Alkaline degreasing: a fundamental phase for the superficial cleaning of the products, from which grease, oil and various impurities are removed; the effectiveness of our pre-treatment is even greater thanks to the immersion phase;
- Activation: the phosphating phase is preceded by the activation phase, which is considered very important as it gives the metal surface properties favourable to the deposition of a microcrystalline and homogeneous phosphatic layer.
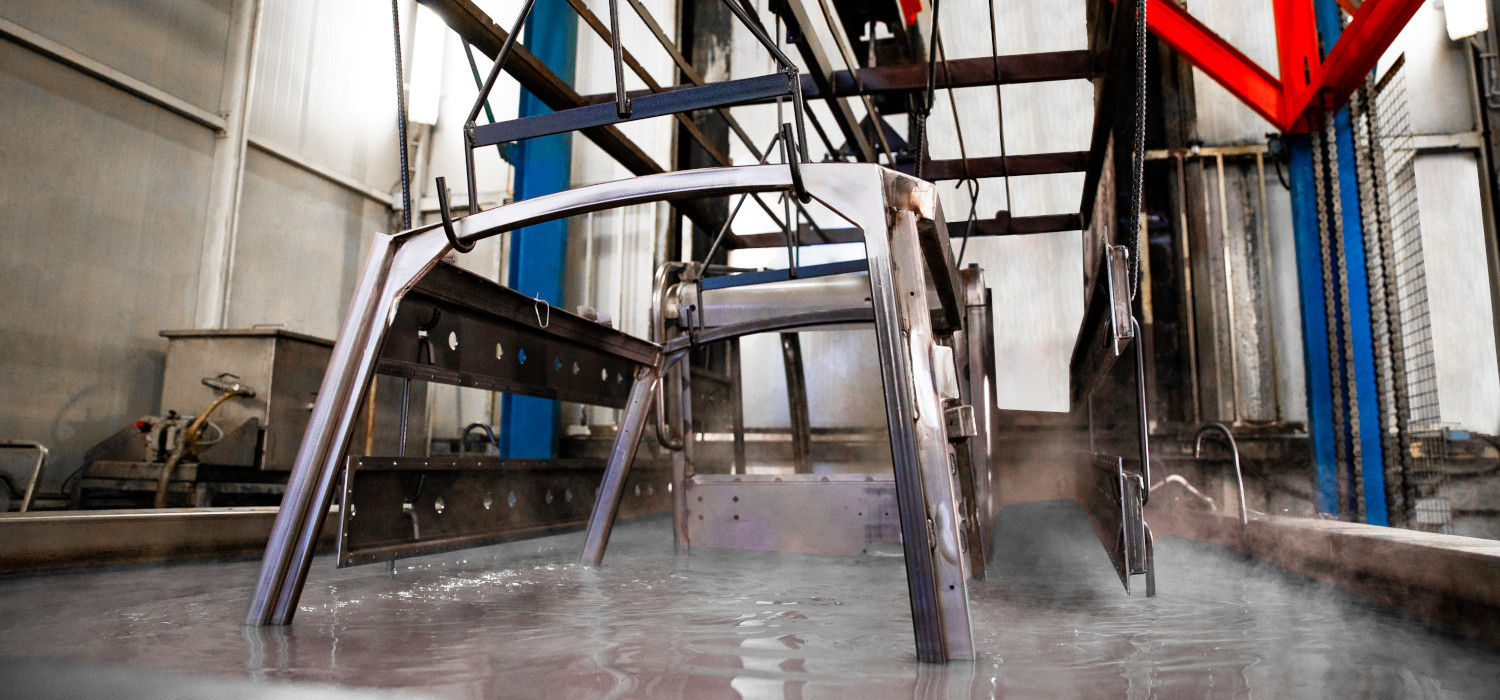

Phosphating is the main pre-coating corrosion protection
There are a number of practical uses that make phosphating an extremely important process, including anti-corrosion protection by oiling, phosphating for cold forming of steels and lubrication to reduce friction between sliding surfaces, such as in the case of gears.
But the case that interests us most is that of pre-coating: phosphating is the most common pre-treatment of metal surfaces in preparation for subsequent coating.
The coating must possess particular properties to be considered qualitatively satisfactory: on the one hand mechanical, with reference to the adhesion between the coat and the substrate, and on the other hand anti-corrosive, linked to resistance to oxidation and rust. Adherence and resistance, as well as correct preparation of the substrate, are also (but not only) influenced by the thickness of the coating, while resistance to corrosion is strongly correlated to the performance of the phosphating pre-treatment.
Phosphating is used when the article has to contend with corrosive environments or agents that tend to impact the durability of the coating; for this reason it is widely used in demanding sectors such as automotive, agricultural machinery, industrial, fluid handling solutions and household appliances.
Among the different types, the best performing is currently the tricationic, composed of zinc, nickel and manganese, because it provides the best results both from a mechanical and an anticorrosive point of view, as well as giving the possibility of being applied both by immersion and by spraying. The result is excellent and the coating will be thin and well compacted.
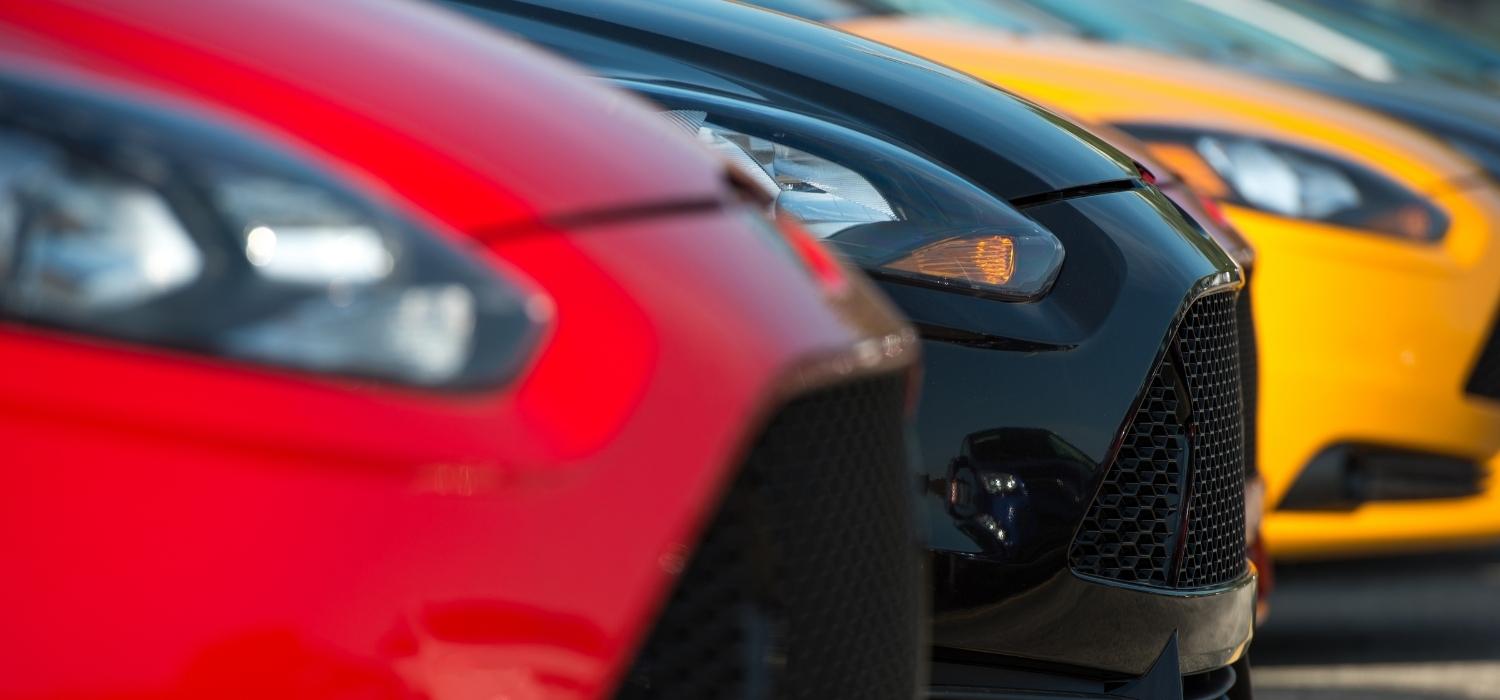

An example of industrial application: the automotive sector
The aesthetic perfection and durability of bodywork is fundamental: bodies affect the first impact people have with cars and the care with which they are made is well known.
Starting from this basic assumption, we understand the importance and the role played by phosphating: in the automotive sector it is always used as a pre-treatment for coating, in order to make the surface as resistant as possible to the propagation of corrosion.
In order to make the body as resistant as possible, a typical automotive coating cycle includes:
- Phosphating;
- E-coating;
- Primer;
- Top coat.
It is worth remembering that zinc phosphating also improves coat adhesion, with a positive impact both in terms of resistance and aesthetic appearance.
Although phosphating has been an established standard in the automotive sector for a long time, nowadays more and more industries have introduced it as a safe way to increase the quality of the coating, protection and ultimately the product itself.
Would you like to receive more information? Write to us at info@zoccaratoverniciature.it.